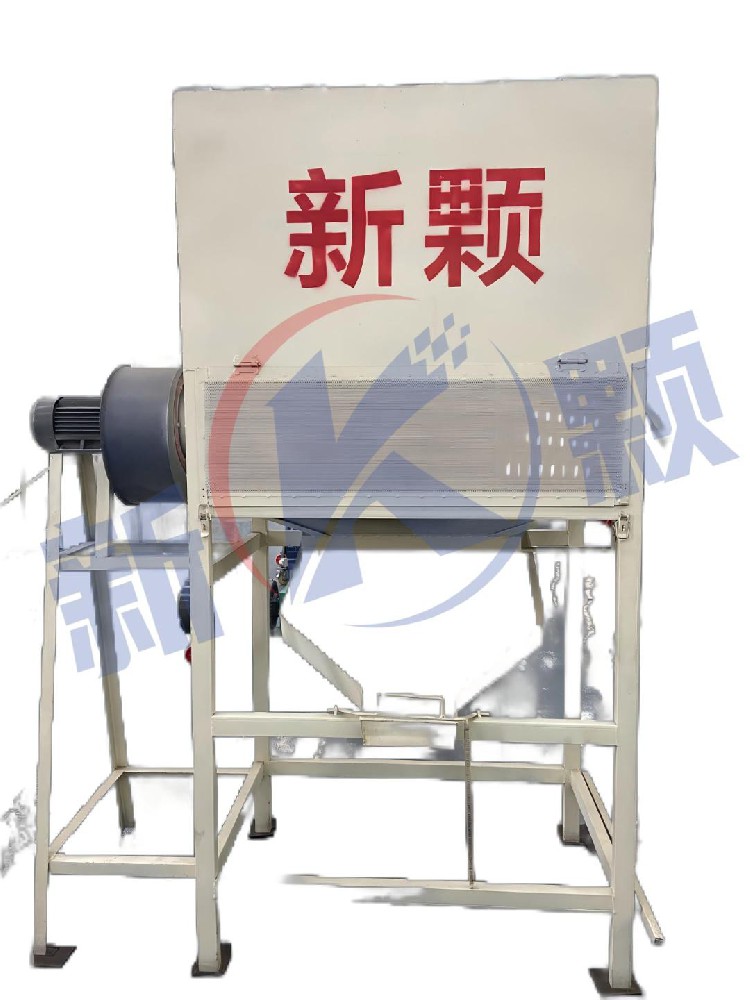




A cooling machine is a device that cools high-temperature objects to the desired temperature through various cooling methods, widely used in industrial production and other fields. The following is a detailed introduction:
1、 Classification and structural characteristics
Air cooled cooling machine:
Structure: Mainly composed of fans, cooling ducts, heat sinks, etc. The fan is used to generate air flow, and the cooling duct guides the airflow through the heat sink. Heat sinks are usually made of metal material with a large surface area and are installed on the surface of objects or heat exchangers that require cooling. For example, in the air-cooled heat sink of a computer CPU, the heat sink is tightly attached to the CPU and the heat is carried away by a fan blowing air.
Working principle: Using air as a cooling medium, the heat of high-temperature objects is transferred to the heat sink through thermal conduction. The flowing air exchanges heat with the heat sink, taking away the heat and achieving cooling. Its cooling efficiency is affected by factors such as air flow rate and temperature, and is suitable for situations where temperature requirements are not particularly precise and heat dissipation is not significant.
Water cooled cooling machine:
Structure: Generally includes a water pump, water-cooled pipes, water tank, radiator, and cooling fan. The water pump drives the coolant to circulate in the water-cooled tubes, which usually surround high-temperature components or pass through heat exchangers. The water tank is used to store coolant, and the radiator and cooling fan work together to dissipate the heat absorbed by the coolant. For example, in the water cooling system of a car engine, water cooling pipes are distributed around the engine cylinder block.
Working principle: The coolant circulates in the cooling system under the action of the water pump, absorbing heat from high-temperature objects. Then, at the radiator, the heat in the coolant is carried away by the air through heat exchange. After the temperature drops, it returns to the vicinity of the high-temperature object to continue absorbing heat, achieving continuous cooling. This cooling method has good cooling effect and can handle large amounts of heat, but the system is relatively complex and requires attention to coolant leakage and maintenance.
Oil cooled cooling machine:
Structure: There are core components such as oil pump, oil cooler, and oil pipe. The oil pump delivers the cooling oil to the high-temperature area, while the oil cooler is a key equipment for heat exchange, reducing the temperature of the oil through methods such as air cooling or water cooling. For example, in the transmission system of some large industrial machinery, oil cooled coolers can cool lubricating oil.
Working principle: The cooling oil absorbs heat from high-temperature components, and then in the oil cooler, it reduces its own temperature through heat exchange with external cooling media (such as air or water), and then returns to the high-temperature components for circulating cooling. The advantage of the oil cooling method is its good tolerance to high temperature environments and high loads, while the oil can also provide lubrication, but the cost is relatively high.
2、 Application Fields
Industrial production: In the metallurgical industry, equipment such as blast furnaces and converters are used to cool high-temperature metal materials and equipment components, ensuring the safety of the production process and the normal operation of equipment. In chemical production, for some materials that have undergone high-temperature reactions or reaction vessels that operate at high temperatures, a cooling machine can quickly cool them down for subsequent processing.
Electronic devices: Components with high heat generation such as CPUs and graphics cards in electronic devices such as computers and servers require cooling machines to ensure that they operate within a safe temperature range and prevent performance degradation or damage caused by overheating. In the electronic equipment of communication base stations, cooling machines also play a crucial role in ensuring stable operation of the equipment.
Mechanical manufacturing: Cutting tools, molds, etc. in the process of mechanical processing will generate heat after long-term operation. Cooling machines can cool them, extend their service life, and improve machining accuracy. At the same time, the oil in the transmission and hydraulic systems of some large machinery also needs to be cooled to ensure the stable operation of the system.
Food processing: In the process of food processing, such as rapid cooling of food that has been sterilized at high temperatures, or for some food that needs to be processed in a low-temperature environment (such as ice cream production), a cooling machine can provide suitable temperature conditions to ensure the quality and safety of the food.
3、 Advantages
Accurate temperature control: The ability to accurately cool high-temperature objects to the desired temperature based on set temperature parameters is crucial for some temperature sensitive production processes and equipment.
Improving equipment lifespan: By promptly removing heat and avoiding damage to equipment components caused by high temperatures, such as reducing thermal fatigue, oxidation, and other issues, extending equipment lifespan and reducing equipment renewal costs.
Improving production efficiency: In industrial production, rapid cooling can shorten the production cycle. For example, in the casting industry, rapid cooling of molds can accelerate the next round of casting production. Meanwhile, a stable temperature environment is beneficial for ensuring consistency in product quality and improving overall production efficiency.
Environmental protection and energy conservation: Modern cooling machines are increasingly focusing on energy efficiency in their design. By optimizing cooling methods and control systems, energy consumption is reduced, and the use and recycling of some cooling media are also more environmentally friendly.
 Scan to consult WhatsApp customer service
Scan to consult WhatsApp customer service  WhatsApp scan code
WhatsApp scan code

Customer Service Hotline+(86)186-3714-5777
7X24H Service Hotline+(86)186-3714-5777
Copyright © 2025 XinKe All Rights Reserved. Add:China Henan Zhengzhou Xingyang, Feilong Road and Xingyun Road,30 meters east and south of the road XML Technical Support